Hydrology section
The Environmental Physics Group conducts extensive research in the field of isotope hydrology and hydrogeology. Employed are methods based on oxygen (18O, 17O, 16O), hydrogen (3H, 2H, 1H) and carbon (14C, 13C) isotopes.
Activities in this field are carried out on behalf of and in cooperation with:
- universities,
- government institutions,
- local water supply companies,
- private geological and hydrogeological enterprises,
- water bottling plants,
- hydrological institutions abroad
- International Atomic Energy Agency in Vienna.
The Environmental Physics Group also conducts scientific research in the framework of doctoral and master's theses.
During the last two years (2018-2019), Environmental Physics Group conducted 38 isotope studies for various domestic institutions.
Major research area in isotope hydrology:
- determining the origin of groundwater,
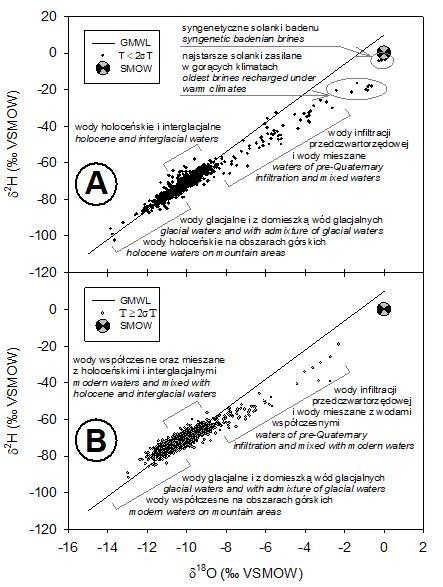
Stable isotope composition of groundwater of infiltration origin in Poland:
A – tritium-free groundwater, B – groundwater containing tritium
- defining recharge areas for mineral and therapeutic waters in mountain areas,
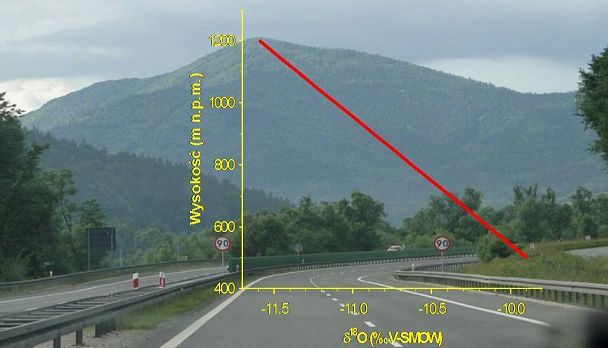
The altitude effect in δ18O for the area of the Polish Carpathians.
- quantifying mixing proportions of different types of water,
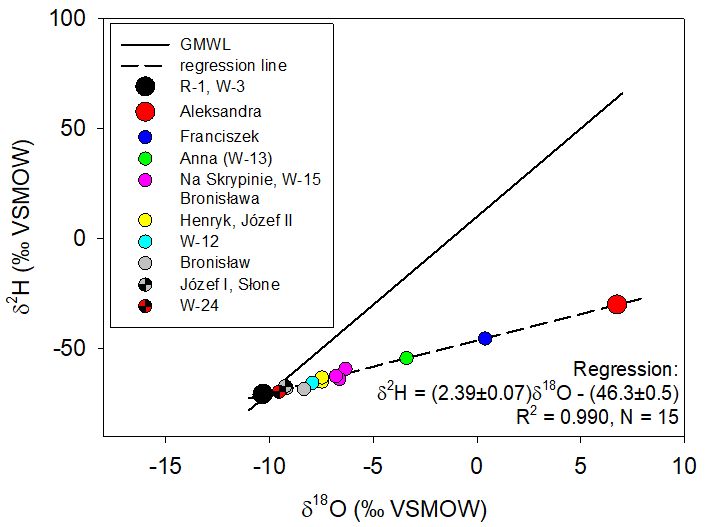
An example of two-component mixing of diagenetic waters (Aleksandra) with modern infiltration waters (R-1, W-3) in the Wysowa area.
- assessment of water hazards in salt mines,
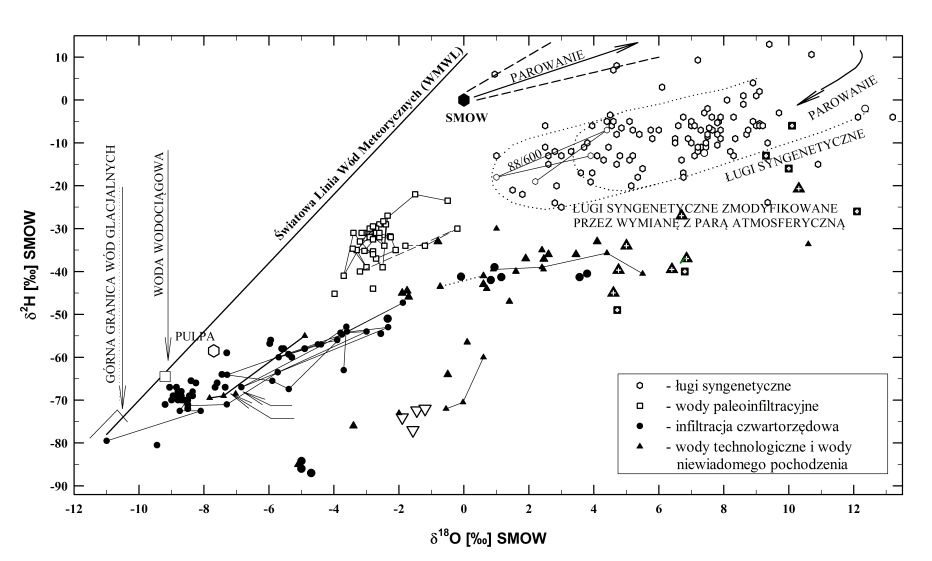
Water types identified in the Kłodawa salt mine.
- groundwater dating:
- tritium method - see drawing for the inflow in Z-32 chamber in the Wieliczka Salt Mine
- radiocarbon method – see a sketch diagram of the dating procedure
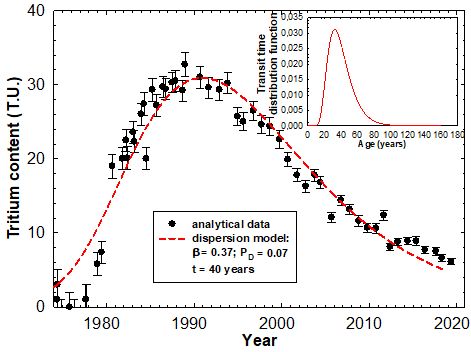
Tritium concentration in inflow to the Z-32 chamber in the Wieliczka Salt Mine. Parameters of the fitted dispersion model of water flow are given also presented.

Sketch diagram of the 14C dating of groundwaters.